一. General Idea
DP ≈ recursion + memorization + guessing
memorize(remember) & reuse solutions to subproblems that help solve the problem.
time = #subproblems * time/subproblem, treating recursive call as Θ(1).
Bottom-up DP algorithm: topological sort of subproblem dependency DAG
often can save space
Guessing: try all guesses and take the best one
Shortest paths:
guess: 既然不知道哪条路到最后的节点最短那就全试一遍,然后选最短的路(无法解决环路问题)
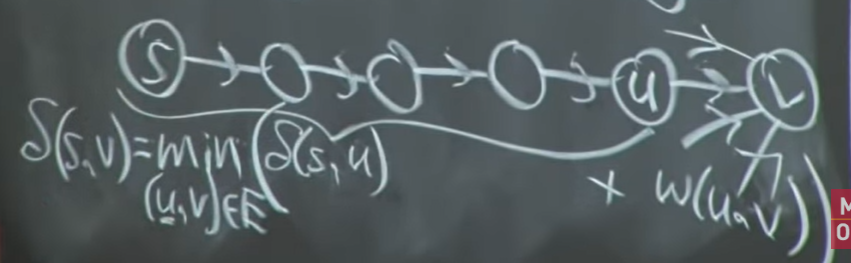
为解决环路问题,引入了k
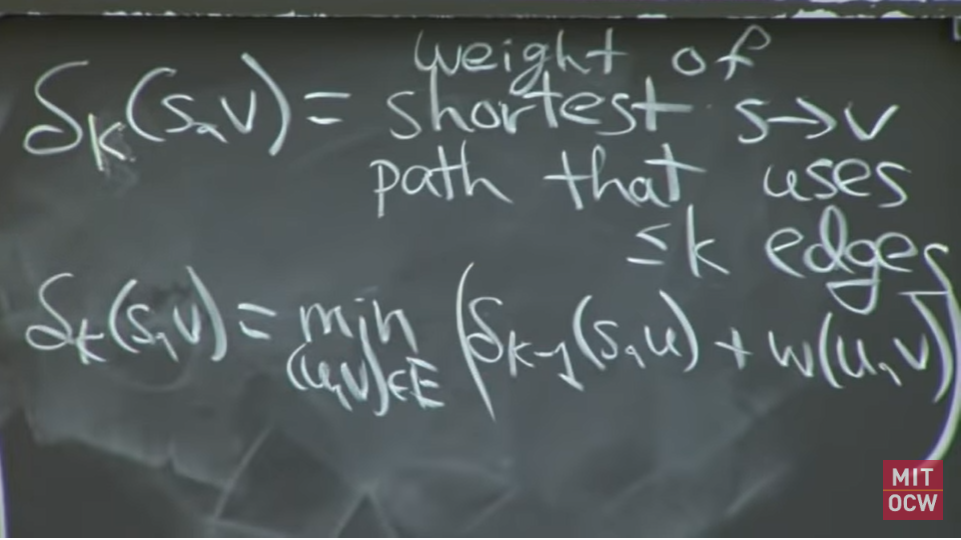
二. 5 “easy” steps to DP:
- define subproblems
#subproblems - guess
#choices for guess - relate subproblem solutions
time/subproblem (similar to #choices for guess) - recurse & memorize or build DP table bottom-up
check subproblem recurrence is acyclic, i.e. has topological order
total time - solve original problem
extra time
三. Subproblems for strings/sequences
- suffixes x[i:] ∀i
- prefixes x[:i] ∀i
- substrings x[i:j] ∀i≤j
once find I need to use both 1 and 2, then mostly I need to use 3
四. Kinds of guessing
1 in 2(&3): guessing which subproblem to use to solve the bigger subproblem
2 in 1: add more subproblems to guess/remember more

Comment